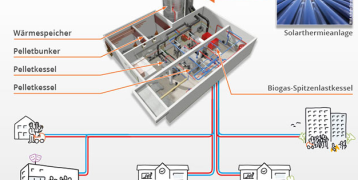
Decarbonising of heating and cooling

Heating and cooling make up a significant proportion of Europe’s final energy use, but only around a quarter of this is provided by renewable resources. Heating and cooling are heavily reliant at present on imported fossil fuels, giving environmental, economic, and geostrategic imperatives for decarbonisation.
With heating being the main energy cost for European households, providing cheap and sustainable energy also has significant social benefits. While the integration of renewables is essential, net-zero in this sector will only be reached with significant improvements in energy efficiency and the use of passive technologies.
The European Union has established a comprehensive policy framework for renewable heating and cooling, with several financial and technical support programmes, though much action is still required to reach targets. Local and regional authorities will play a key role given that heating and cooling strategies are highly dependent on local conditions and resource availability.
In this policy brief, you can explore current use of renewable energy for heating in Europe, EU legislation and support as well as inspiring good practices from Interreg Europe projects such as POTEnt, CLEAN, APPROVE, BUILD2LC and SHREC.
Download the policy brief
Access the full policy brief below to discover good practices as well as information on the EU legislation and support.
Policy brief on decarbonising heating and cooling
Featured good practices

Replacing of cooling-heating systems at Iasi Municipality during Covid Pandemic
Taking into consideration the limited presence of the public officers and citizens during pandemic to its own premises, Iasi Municipality engaged significant works of rehabilitation and managed to...

From Stump to Boiler, Bioenergy educational environment